The Useful Income Statement Template
author
Lumin staff
published
Dec 18, 2025
categories
Small business
read time
5 mins
An income statement is the primary operating report that shows how much profit you have received over a period. With the help of this report, you will learn how to increase your company's profit and better control your finances.
Table of Contents
1. The objectives of generating an income statement
2. Statement of income and expenses is the king of financial statements
3. Income statement structure
4. Critical financial statements and what they are for
5. Statement of Financial Performance (P&L)
6. A quick checklist of financial conditions
7. When reporting, remember...
- 1. The objectives of generating an income statement
- 2. Statement of income and expenses is the king of financial statements
- 3. Income statement structure
- 4. Critical financial statements and what they are for
- 5. Statement of Financial Performance (P&L)
- 6. A quick checklist of financial conditions
- 7. When reporting, remember...
share this post
Income statement templates reflect income and expenses as well as net profit and losses of the enterprise for the current period. The statement portion of the comprehensive income template is the public documentation of the enterprise — it can be published in print, sent by email, or transferred to shareholders.
The objectives of generating an income statement
At its core, the income statement is a measure of the performance of an enterprise during the reporting period. This document is provided to investors and creditors, who, with its help, can predict the volume of cash receipts in the near future; income statements and balance sheet templates are also offered to shareholders. The primary purpose of generating an income statement is to provide the necessary financial information to those people who are interested in the company's performance.
From a simple financial statement sample, it is clear how a business works: sales revenue by type of product and business. If you need information on the sales of goods from different manufacturers and/or information on differing materials, you can review the business income statement template, which allows you to see which products are top-sellers and which are not and which manufacturers are better to work with. As income statement templates highlight what product points are operating at a loss, every month, it is recommended that you make a management decision, such as closing, investing more money in development, supplementing the assortment, etc. The Operating Profit will show the financial result of the month, and the Net Profit shows what amount can be disposed of.
Having analyzed the income statement template, you can:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of top management
- Make a forecast of the future activities of the enterprise
- Distribute dividends among shareholders
- Assess the amount and structure of expenses relating to the enterprise
- Compare the amount and structure of expenses of the enterprise with the previous period
- Establish the factors that most affect the final financial result
Statement of income and expenses is the king of financial statements
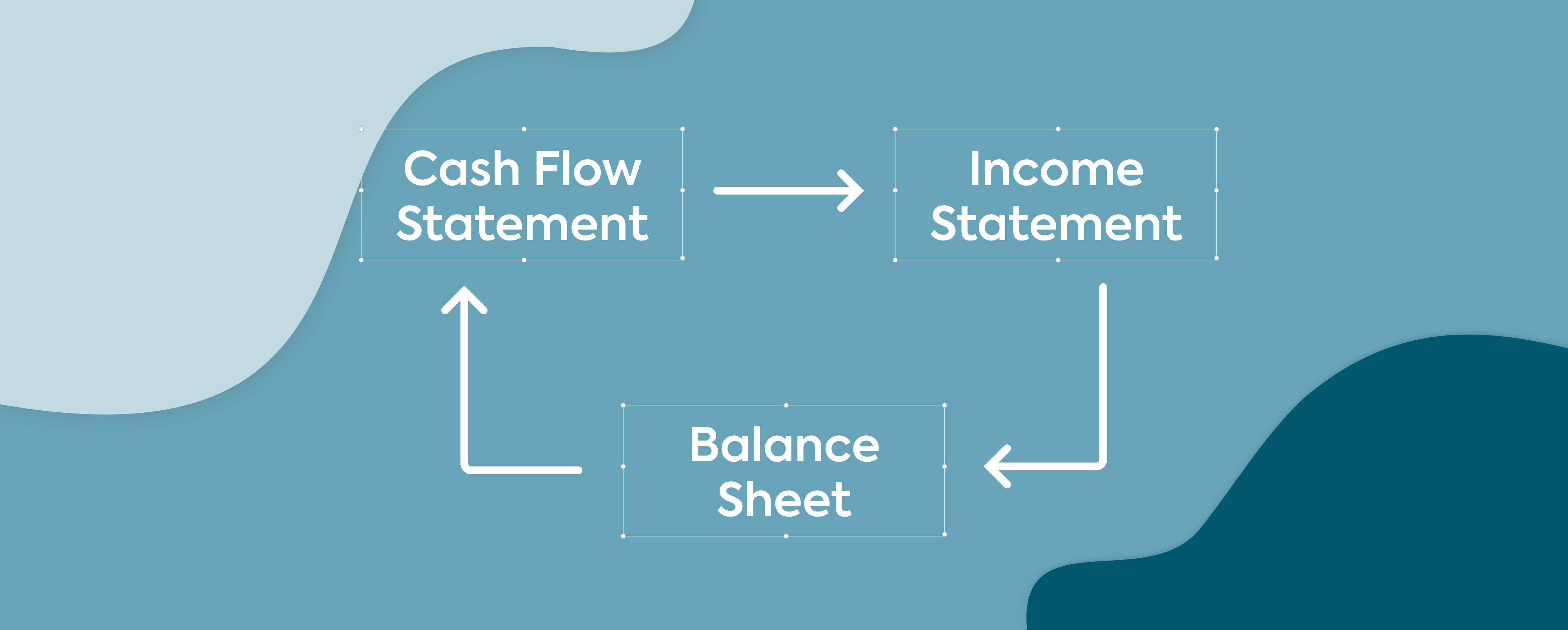
There are three primary financial statements: Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements, and Balance Sheets. You could say that, together, all three of these reports form a business control panel. The balance sheet shows the financial position of the company for a specific date, the financial statement shows the financial results of the company for a certain period, and the statement of cash flow displays the directions the cash is circulating around the company.
- The income and expense report is a speedometer that shows how fast the business is moving, how much profit you have earned, and how efficiently the company is developing.
- Think of the cash flow statement as a measure of fuel. Do you have enough money to get where you need to go?
- The Balance sheets are like the internal components of the "operating system" of a car — ensuring all systems are in order and maintaining ratios.
The income and expense statement is the primary operating income statement template that shows how much profit you have received over a period.
Income statement structure
Each company has its structure of the income statement. Management reporting is created for each company and has its unique features. It is recommended that the ODR contains the following sections:
- Revenue: Revenue (shipping) of the company for the period. It is better to break it down by types of activity or by groups of goods for which you need to control marginal profit (profitability).
- Direct expenses: the expenses directly related to the revenue that you indicated in your income statement. Without revenue there would be no such expenses.
- Direct costs: This is the cost of the shipped goods, that is, the amount for which you bought the exported goods from the supplier. Include in the direct costs only those expenses that you can calculate by the direct method, for example, materials, salaries and services. Fees related to several types of products are best taken into account for individual cost items.
- Production costs:the expenses directly related to the production cycle: salaries of production personnel, rental of a workshop, production services and so on. These expenses are considered conditionally constant. Sometimes they depend on revenue, for example, the electricity of the workshop or piece-work wages of workers, but for the most part, they are constant.
- General business expenses: Expenses for servicing your core business: accounting, financial services, marketing, and managerial salaries, HR and services — these are fixed costs that do not depend on the amount of revenue.
- Expenses for financial activities: These are the expenses for raising borrowed capital.
Critical financial statements and what they are for
When it comes to finance, managers and owners recall the three necessary financial reports that are a must-have for any business. Unfortunately, for the most part, they often don't know how to analyze and compile them, which can be misleading.
Before starting to consider each income statement template separately, I would like to remind you that there are two ways to account for income and expenses: accrual and cash. Many entrepreneurs tend to think of their financial results on a cash-only basis, which is fundamentally wrong.
The difference between these methods consists of the practice of recording income and expenses for the selected accounting period, in which business transactions for the period are considered liabilities and which are income. It is clear that for the entire existence of the enterprise, all cash receipts are income and all payments are expenses; however, we are not interested in the whole picture but a specific part of it: a quarter, a month, a week, or even a day. When we break our timeline into segments, a difference arises.
In the cash method, income is any cash flow to the cash desk or a current account, and expenses are any payments or payments made in the accounting period. At the same time, the relationship between income and expenses for the same period does not matter: we bought water, sold an hour of karaoke — it's all still income and spending.
In the accrual method, income for a period is considered to be the sale value of goods and services sold, rendered in that period regardless of the payment method. The cost refers to the cost of products and services sold, as well as the company's consumption of goods and services, regardless of their payment to the supplier. If the income was a soup, then the ingredients related to the soup are considered to be expenses: food, cook salary, hall rental, electricity, etc; all of this leads to the possible realization of this particular soup.

Which method is best depends on the situation. The cash method is more natural to execute because —based on data from payment systems, which are very easy to collect — they are reflected in the cash or banking system and are always confirmed by primary documents. Also, the result of this method - profit - coincides with the cash balance, i.e. it can be easily checked (by cash recount). The accrual method is more complicated and its profit does not coincide with the cash balance. Still, it is more accurate in the sense that if the profitability or the efficiency of the company's activity are taken from the profit received, then it makes more sense because income, expense, and profit are all interconnected.
The difference between them can be illustrated by the example of gasoline consumption in a car. Gasoline consumption is a specific indicator that we use to measure the "efficiency" of a car (and driving style). The lower the gas mileage, the better.
An "accrual method" is found when we compare the distance traveled over a period of time with the amount of gasoline consumed over the same period. For this, we use an on-board computer. We can drive 100 miles in one week and use 7 liters (7 L / 100miles). Another week, we could drive 100 miles and consume 60 liters (6 L / 100miles). Obviously, in the second week, we drove more economically or "more efficiently."
The "cash method" is if we compare the distance traveled over a period of time with the volume of gasoline purchased for the same period. We could use 50 gallons in one week and drive 1 mile (5000 gallons / 100miles), and next week add another 1 gallon and drive 100 miles (1 gallon / 100miles). The results are not comparable, and they make no sense. This leads to a straightforward conclusion: profit is not equal to cash in hand.
For the analysis of the "money" indicator, a cash flow statement is used; for the study of the "profit" indicator, the profit and loss statement is used.
Statement of Financial Performance (P&L)
This income statement has many names, but it has one essence: the display of the financial result of activities for a certain period and a breakdown of the components of income and expenses. The items of income and expenses in the management profit and loss template on financial results can be detailed to the required level, but the structure will remain so. This profit and loss statement template is prepared on an accrual basis and not on the cash inflow or outflow. If you make it up for money, then this is no longer P&L.
Take, for example, sales revenue. It is considered to be a fulfilled obligation upon the shipment of goods, with the provision of services. Acts of signed services or expense invoices confirm revenue. Revenues are the proven net of indirect taxes (for example, tax).
What the manager needs to know about profit and loss statement templates:
- The profit and loss template must be filled
- Revenues and expenses are shown on an accrual basis
- You should adhere to the rule of periods: expenses are recognized simultaneously with the income for which they were incurred, especially concerning the cost of inventories
- Indirect taxes are not involved in the formation of the financial result (keep in mind— this rule has exceptions)
- The connection of the income statement with the balance sheet
Under no circumstances do the profit and loss account and balance sheets replace each other— they perform different functions. The balance sheet, as already mentioned, shows the financial position of the company at one time or another and is a "snapshot" of the company's assets. A statement of profit and loss shows the flow of earnings for the period. There is a direct link between the two reporting forms.
The income statement relates balances at the beginning of the period and the end of the reporting period. In other words, at the beginning of the new reporting period, the balance sheet shows the initial financial position of the company. After some time, a profit and loss statement is prepared, showing how much profit the company received for the period and a balance sheet reflecting the new financial position of the company at the end of the period. This balance shows the changes that have occurred since the date of the previous balance.
A quick checklist of financial conditions
To quickly conclude whether everything is going according to plan or if you urgently need to intervene, you can determine your break-even point. To determine this point, simply calculate the number of direct expenses by the example of the previous period, identify the average margin for actual shipments and understand what revenue you minimally need to cover fixed costs.
- Control margin profitability: Any minor deviations in the margin will result in substantial losses in net profit.
- Analyze marginal profit: Organize this by product groups (types of activity). Maybe there is something that gives you a low margin, and if you also use borrowed funds for this type of business, then, in the end, there may be a loss from this direction.
- Set the minimum value: Set the minimum value of margin profits low so you can offer promotions and discounts.
- Analyze the value of fixed costs: Group the production and general costs for the last three periods. Remember to set the number of fixed costs.
- Control not only the absolute value: Control not only the absolute value of each expense item but also the relative — what share in the revenue is the expense item? Variable costs should change in proportion to the revenue, and the share of fixed costs should decrease with increasing shipping.
- Plan your income and expenses: Track deviations monthly.
When reporting, remember...
Performance analysis is not an easy task, and complexity increases with business growth. The statement of comprehensive income should be:
- Structural — reporting is a system, and it should be tightly woven into the structure of your company.
- Sufficient — it should not be redundant. Here is an excellent example of how it's done.
- Valuable — it must be compiled if used, otherwise it is meaningless. DO NOT report for the sake of the report itself.
- Authentic — you must trust the numbers in the statements.
- Timely — detailing the reports is good, but if it is completed, and the need for it has disappeared, then such a report is not needed.
Drawing up the correct structure of financial statements, identifying financial holes, and suggesting ways to eliminate them is a task for a professional. If your company does not have a commercial director, then perhaps you do not own all the necessary financial information. The solution to this problem may be the transfer of financial accounting to outsourcing, or using a foolproof template.
share this post