Are you doing a last-minute reference check?
author
Lumin staff
published
Apr 15, 2024
categories
Article
read time
5 mins

Information noise, constant media wars, and an abundance of fakes make the work of a journalist committed to high-quality standards in the profession unbearably tricky today. How can we check facts in our challenging digital age?
Table of Contents
1. Here are our hacks to save stress and get assignments in on time.
2. What is fact-checking?
3. Facts versus factoids
4. A critical approach
5. Why check facts?
6. Employee reference and background check
7. Fact-checking when working on a scientific article
8. What to look for when preparing a scientific article
9. Five basic rules of fact-checking
- 1. Here are our hacks to save stress and get assignments in on time.
- 2. What is fact-checking?
- 3. Facts versus factoids
- 4. A critical approach
- 5. Why check facts?
- 6. Employee reference and background check
- 7. Fact-checking when working on a scientific article
- 8. What to look for when preparing a scientific article
- 9. Five basic rules of fact-checking
share this post
Here are our hacks to save stress and get assignments in on time.
Information noise, constant media wars, and an abundance of fakes make the work of a journalist committed to high-quality standards in the profession unbearably tricky today. How can we check facts in our challenging digital age? We live in post-truth and are always influenced by the algorithms of technology platforms, on the one hand, as well as personal cognitive distortions on the other. And all this in a toxic media environment with mass authorship. Under such conditions, the skills of checking references and checking resources are invaluable. If you know how to navigate information flows, catch fakes, verify information, expose manipulations, you become a more valuable asset professionally. Reference check and fact-checking help develop:
- Skills in working with sources and critical perception of information
- Skills for individual and group work in fact-checking
- An understanding of the principles of fact-checking, information verification, and the logic of research projects
What is fact-checking?
The concept of fact-checking came from traditional journalism. More precisely, from the editorial office's principles, an editorial filter is a necessary condition in the technology of any research work. Today you can use a reference check template or even reference check tool. This technology is beneficial to ethical principles in any work with information. Modern tech, like a PDF tool that has an option to add annotation to PDF or reference check app or even reference check questions template, helps you uphold objectivity, impartiality, and accuracy of any researcher.
A fact is an event supported by reliable evidence. Different people may have different views on the same event, but you can't argue with the facts. That is why the fact should not only be established but verified, rechecked, and "cast in stone."
- Fact: The ancient Egyptians built the Giza pyramid complex.
- Not a fact: The pyramids were built by the people of Atlantis or aliens or even representatives of an unknown ancient civilization.
- Explanation: Not far from the pyramids, archaeologists have discovered a builders' settlement, and next to it - a necropolis. To date, more than 1,000 skeletons have been studied. Anthropologically, they coincide with the population of modern Egypt. It is characteristic that many skeletons have numerous injuries and fractures. This is due to industrial accidents.
The antipode of a fact is a factoid. This is dubious information, widely accepted as the truth. The danger false facts pose, for example, in the media gets a quick response and spreads quickly. Further rebuttals don't get as much coverage as fakes. Distortion of facts is a crime against objectivity and accuracy. It is worse if it is a deliberate crime against independence and impartiality. It's terrible when it's a deliberate manipulative construct. By employing checking-reference procedures and tools in fact-checking is the only weapon against fake news, unverified data, typos, distortions, pseudoscience, and other obscurantism.
Facts versus factoids
In the era of digital communications, the concept of "factoid" is becoming more and more relevant. This is an initially non-existent fact published in the media and receives a quick reaction and assessment. And they, in turn, affect the picture of the world and people's actions. The truth doesn't matter if the effect is real.

Due to lack of checking references and checking resources, various phenomena and events are actualized and legalized. Unconsciously or prudently, they are embedded in the form of "confirmed" facts in the information picture. As a result, they were distorting the entire canvas. This technique is actively used by propagandists, cyber fighters, network trolls, and other manipulators of all sorts.
A critical approach
The fact-checker's primary weapon is doubt (and reference check app.) Professional distrust, reality check and even PDF tools with an option to add annotation to PDF or reference check template make all the difference when working with data and text. Here, the logic and toolkit of mainly fact-checking coincide with the methodologies and technologies of scientific work. Moreover, a course on source studies specializing in historians can raise the quality of any work with data, work with multiple data sources etc.
Why check facts?
Let's see why you need to check facts at all. The main reason: false facts give a false picture of the world. This, in turn, casts a shadow on your reputation. It is easy to lose trust; to regain it isn't as easy. To understand the severe consequences of poor-quality fact-checking or its absence, here's an example:

Pakistan has threatened Israel with nuclear weapons in response to fake news. In December 2016, Khawaja Asif tweeted that Israel, threatening Islamabad with nuclear weapons, forgets that Pakistan has them. This is how the Minister of Defense reacted to the publication of AWD News, a site with fake news. The publication's headline read: "Israeli Defense Minister: If Pakistan sends troops to Syria under any pretext, we will destroy it with a nuclear strike." By the way, the authors of the yellow article wrote about Moshe Ya'alon, who was the former, not current, minister of defense. They also mixed up several other positions. The Israeli Defense Ministry, in turn, replied that Ya'alon never made such statements. And she noted that the story Asif refers to is entirely fictional. The misunderstanding was finally settled.
Employee reference and background check
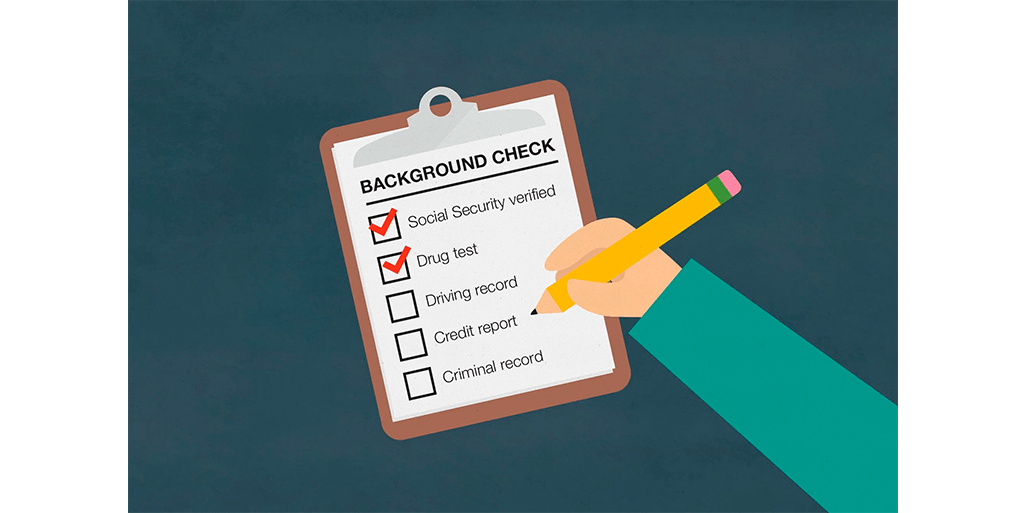
In the practice of hiring personnel, there is the concept of "Pre-Employment Screening," which is basically fact-checking for a very specific purpose. The "checkpoints" may vary. Usually it includes many checks. Different people often put different concepts in terms of Background Check, Validation Check, and Reference Check, etc. Of the main types of checks:
- Criminal Background Check is a check of information on the presence of criminal records, being under investigation, etc. The results of this activity include a certificate of the presence/absence of convictions. For Ukraine, it can be obtained from the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
- Education Check - Confirmation of the authenticity of educational documents. You can check in the archive of the corresponding university or through the technical administrator. This is only confirmation that the given educational document was issued and issued to this particular person.
- Financial Check - Information on the availability of outstanding/overdue loans, credit history, if such information is legally available in a particular country.
If we restrict the concept of "Background Check" only to these 3 points, as it was before, the result obtained is quite unambiguous and objective, since it is nothing more than a list of documented facts."Pre-Employment Screening" may include such processes as:
- Reference Check - receiving feedback and characteristics from previous jobs/service/study
- Validation Check - monitoring news feeds and social networks for any additional information about the applicant, such as positive and negative

The use of reference checks by many companies and studies is recognized as an extremely ineffective way of collecting information because the statistical reliability of the results of such a check is often lower than the reliability of the data provided by the applicants. There is a liability for the provision of inaccurate data by former employers. Hence, their employers try not to say too much, so that later they are not sued by the former employee or his new employer for providing false information that led to hiring/refusal to hire. To avoid such issues you can use the reference check template and the reference check questions template. All of these and other types of checks are often referred to for simplicity as "Background Check" instead of "Pre-Employment Screening," which creates confusion in terms. There is no single clear list of checks. Each company determines a list of those checks that they want to carry out and then hire employees or contract a third-party company that covers this set.
Fact-checking when working on a scientific article
During the writing of a scientific article, many pitfalls arise in the path of the author. Near-scientific information presented as scientific work, research not confirmed by practical experiments, manipulation of facts, non-authentic data and outright lies - such information regularly sneaks into not only journalism and resumes but also the scientific environment. The use of such information in research leads to the collapse of the reputation of a researcher. This, in turn, entails sad results: an unprotected thesis, a failed dissertation, a loss of trust, and authority among colleagues.
Fact-checking in journalism is aimed at protecting copyright publications and important data from gossip, artificially manufactured data, or disinformation. In the scientific community, fact-checking is directed in a slightly different direction. It is aimed at:
- Eliminating pseudo-scientific information presented as reliable facts;
- Checking the results of research in the context of a crisis of reproducibility - this is, unfortunately, a fairly common phenomenon when articles with unverified research results are published;
- Using only factual non-distorted data;
- Avoid the manipulation of facts, that is, the deliberate arrangement of facts in such a way as to bring the reader to a conclusion favorable to the author;
- Escape manipulation of public opinion, that is, the desire to embellish facts, distort them in such a way as to push readers to the desired decision.
What to look for when preparing a scientific article

Fact-checking is used at all stages of research preparation, like checking resources at the beginning and using citation machine plagiarism at the end. Otherwise, due to critical errors that were not noticed initially, the author will have to rewrite at least several sections.
- Preparation of reference material: Before starting to write the article itself, the researcher prepares the critical reference material, which he will later use to write his article or dissertation. At the same time, it is necessary to pay attention to such inaccuracies as incorrect references to sources, references to outdated documents or scientific works.
- Checking drafts: In writing, the material is supplemented with new data, which must be correctly woven into the canvas of scientific work. After completing the draft, it is necessary to check the consistency of all data and results again and pay attention to the following: incomplete quotations, taking out of context and free interpretation of quotations, confusion in new professional terms, or incorrect indication of the historical data in connection with the transition to the Gregorian calendar in 1918. If you use the names of cities or countries, pay attention to their relevance.
- Post-publication fact analysis: After publication, the author continues to supplement the article with minor clarifications, confirms or refutes the controversial information. However, if the first two steps are done in good faith, the third step is not always necessary.
Five basic rules of fact-checking

- Recognize other people's mistakes: Errors are not just about falsifying results and simulations. It also includes negligence, typos, and technical errors. Authors may misspell names, professions, titles, scientific terms. It would help if you had a PDF tool that allows you to add annotation to PDF, or a reference check tool to ease your critical thinking process and to recognize such mistakes in time.
- Look for official sources: Or use several independent sources. The reliability of facts and events can be found in encyclopedias, monographs, and narrow-profile reference books. Also, look for information on the official websites of the figures and their pages on social networks. It is better to be wary of publications in scientific journals. Before using information, make inquiries about the author of the article.
- Ask all parties for their opinion: If the question is about controversial theories or statements, it would be wise to ask colleagues from different scientific schools who hold different views. Thus, the author will be able to objectively approach the description of such issues and avoid gross oversights.
- Always double-check your sources: Impartiality and doubt are the main allies when checking information for relevance. Criticize the information and seek additional evidence for the results described in the source. At this point you can use a PDF tool with the option to add annotation to PDF, a reference check app or even a reference check template.
Fact-checking is, first of all, the responsibility, interest and indifference of the author to his work. On the one hand, Internet communications are scientific databases, publications on social networks, electronic libraries, and communication with scientists from all over the world can significantly speed up and improve scientific work. But on the other hand, a large amount of information does not mean its quality is good. A large amount of unconfirmed or even anti-scientific data forces modern scientists to filter information, analyze, and double-check the data.
share this post